“PGR mouse monoclonal antibody, clone UMAB137, 100 uL/ 30 uL” foi adicionado ao seu carrinho. Ver carrinho
Purified HER2 (ERBB2) mouse monoclonal antibody, clone UMAB36, 100 uL/ 30 uL
R$12.423,26
| Imunógeno | Fragmento de proteína recombinante humana correspondente aos aminoácidos 676-1255 de ERBB2 humano (NP_004439) produzido na célula HEK293T. |
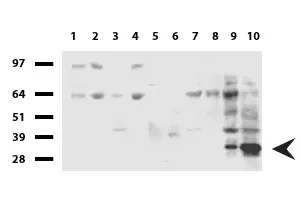
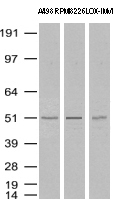
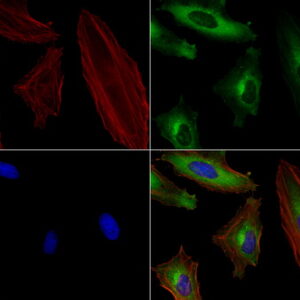
| Aplicações | WB:1:500, IHC:1:50, IF:1:100 |
| Aplicações2 | WB, IHC |
| Resumo | Este gene codifica um membro da família de receptores do fator de crescimento epidérmico (EGF) de receptores de tirosina quinases. Esta proteína não possui domínio próprio de ligação ao ligante e, portanto, não pode se ligar a fatores de crescimento. No entanto, ele se liga firmemente a outros membros da família de receptores de EGF ligados ao ligante para formar um heterodímero, estabilizando a ligação do ligante e aumentando a ativação mediada por quinase de vias de sinalização downstream, como aquelas envolvendo proteína quinase ativada por mitógeno e fosfatidilinositol-3 quinase. Variações alélicas nas posições de aminoácidos 654 e 655 da isoforma a (posições 624 e 625 da isoforma b) foram relatadas, com o alelo mais comum, Ile654/Ile655, mostrado aqui. A amplificação e/ou superexpressão deste gene tem sido relatada em vários cânceres, incluindo tumores de mama e ovário. O splicing alternativo resulta em várias variantes de transcrição adicionais, algumas codificando diferentes isoformas e outras que não foram totalmente caracterizadas. |
| Formulação | PBS (pH 7.3) contendo 1% BSA, 50% glicerol e 0.02% azida sódica. |
| Purificação | Purificado a partir de fluidos de ascite de camundongo por cromatografia de afinidade |
| Isotipo | IgG1 |
| Reatividade | Humano, Camundongo, Rato, Macaco |
| Hospedeiro | Camundongo |
| Tamanho | 137.7 kDa |
| Tipo | UltraMAB |
| Concentração | 1.24mg/ml |
ErbB1-dependent signalling and vesicular trafficking in primary afferent nociceptors associated with hypersensitivity in neuropathic pain.
Rory Mitchell, Marta Mikolajczak, …, Sue Fleetwood-Walker
“Abstract: Effective analgesic treatment for neuropathic pain remains an unmet need, so previous evidence that epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors (EGFRIs) provide unexpected rapid pain relief in a clinical setting points to a novel therapeutic opportunity. The present study utilises rodent models to address the cellular and molecular basis for the findings, focusing on primary sensory neurons because clinical pain relief is provided not only by small molecule EGFRIs, but also by the anti-EGFR antibodies cetuximab and panitumumab, which are unlikely to access the central nervous system in therapeutic concentrations. We report robust, rapid and dose-dependent analgesic effects of EGFRIs in two neuropathic pain models, matched by evidence with highly selective antibodies that expression of the EGFR (ErbB1 protein) is limited to small nociceptive afferent neurons. As other ErbB family members can heterodimerise with ErbB1, we investigated their distribution, showing consistent co-expression of ErbB2 but not ErbB3 or ErbB4, with ErbB1 in cell bodies of nociceptors, as well as providing evidence for direct molecular interaction of ErbB1 with ErbB2 in situ. Co-administration of selective ErbB1 and ErbB2 inhibitors produced clear evidence of greater-than-additive, synergistic analgesia; highlighting the prospect of a unique new combination therapy in which enhanced efficacy could be accompanied by minimisation of side-effects”.
Prediction model of lymphovascular invasion based on clinicopathological factors in Chinese patients with invasive breast cancer
Sandi Shen, Guihua Wu, …, Haibo Zhou
“2.3 ImmunohistochemistryEach TMA block was cut into 2.5-μm thick sections that were stained with the monoclonal antibodies ER, PR, HER-2, Ki67, EGFR, VEGF, E-cadherin, and P53. All the antibodies were ready-to-use from OriGene. A positive control was taken from a breast cancer tissue sample with positive IHC staining results, and a negative control was taken from a paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissue sample that had not been submitted for incubation with primary antibody. The alkaline phospha”
Functional role of RRS1 in breast cancer cell proliferation. Functional role of RRS1 in breast cancer cell proliferation
Jinlian Song, Zhongliang Ma, …, Lin Hou
“2.2 IHC analysisAll formalin‐fixed and paraffin‐embedded sections were analysed by IHC. Primary antibodies were used against the following targets: RRS1 (1: 1000; Abcam, Cambridgeshire, UK), p53 (1: 300; OriGene, Shanghai, China), ER (1: 300; OriGene), PR (1: 300; OriGene), HER2 (1: 300; OriGene) and Ki67 (1: 300; OriGene). The percentage of tumour cells positively stained for each antibody was semi‐quantitatively estimated. The staining intensity of RRS1 expression was scored according to the f”
Produtos relacionados
-
R$12.423,26Adicionar ao carrinho
Imunógeno Proteína recombinante humana de comprimento total de MS4A1 humana (NP_068769) produzida na célula HEK293T. Aplicações IHC 1:100, Aplicações2 IHC Resumo Este gene codifica um…
-
R$12.423,26Adicionar ao carrinho
Imunógeno Fragmento de proteína recombinante humana correspondente aos aminoácidos 311-482 de TYMP humano (NP_001944) produzido em E. coli. Aplicações IHC 1:100, Aplicações2 IHC Resumo Este…
-
R$12.423,26Adicionar ao carrinho
Imunógeno Fragmento recombinante expresso em E. coli correspondendo aos aminoácidos 240-390 de CK19 humana Aplicações WB 1:1000, IHC 1:50, IF 1:100 Aplicações2 WB, IHC Resumo A queratina 19 é um membro da família da queratina. As queratinas são proteínas de filamentos intermediários responsáveis pela integridade estrutural das células epiteliais e são subdivididas em citoqueratinas e queratinas capilares. As citoqueratinas do tipo I consistem em proteínas ácidas que estão dispostas em pares de cadeias de queratina heterotípicas. Ao contrário de seus parentes relacionados, esta menor citoqueratina ácida conhecida não está emparelhada com uma citoqueratina básica nas células epiteliais. É expresso especificamente na periderme, a camada superficial transitória que envolve a epiderme em desenvolvimento. Formulação PBS (pH 7.3) contendo 1% BSA, 50% glicerol e 0.02% azida sódica. Purificação Purificado a partir de fluidos de ascite de camundongo por cromatografia de afinidade Isotipo IgG1 Reatividade Humano, Cão Hospedeiro Camundongo Tamanho 43.9 kDa Tipo UltraMAB Concentração 0.5-1.0 mg/ml -
R$12.423,26Adicionar ao carrinho
Imunógeno Fragmento recombinante expresso em E. coli correspondendo aos aminoácidos 240-390 de CK19 humana Aplicações WB 1:500~1000, IHC 1:50, IF 1:100 Aplicações2 WB, IHC Resumo A queratina 19 é um membro da família da queratina. As queratinas são proteínas de filamentos intermediários responsáveis pela integridade estrutural das células epiteliais e são subdivididas em citoqueratinas e queratinas capilares. As citoqueratinas do tipo I consistem em proteínas ácidas que estão dispostas em pares de cadeias de queratina heterotípicas. Ao contrário de seus parentes relacionados, esta menor citoqueratina ácida conhecida não está emparelhada com uma citoqueratina básica nas células epiteliais. É expresso especificamente na periderme, a camada superficial transitória que envolve a epiderme em desenvolvimento. Formulação PBS (pH 7.3) contendo 1% BSA, 50% glicerol e 0.02% azida sódica. Purificação Purificado a partir de fluidos de ascite de camundongo por cromatografia de afinidade Isotipo IgG1 Reatividade Humano Hospedeiro Camundongo Tamanho 43.9 kDa Tipo UltraMAB Concentração 0.5-1.0 mg/ml